 Strokes and Brain Injury
Strokes and Brain Injury
Strokes that result in brain injury are unfortunately all too common. Over a million people in America experience a stroke every year and frequently damage to the brain during the stroke creates physical and cognitive deficits. Strokes are often called a “brain attack.” Typically strokes require some form of rehabilitation after release from the hospital.
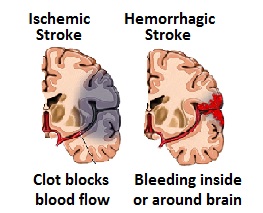
The most common type of stroke causes an interruption to the flow of oxygen to the brain resulting in cell death. Strokes can also happen when a blood vessel bursts, flooding the brain with blood. In either scenario brain damage often happens. They are called acquired brain injuries, due to a medical cause, not something you are born with.
There are two primary types of stroke: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic.
 Ischemic Strokes
Ischemic Strokes
These strokes occur when there is inadequate blood flow to the brain due to some type of blockage inside a blood vessel. Another term for the subtypes of ischemic stroke is “infarct.” When the blood flow is reduced or stopped due to a blockage, the brain cells surrounding the vessel are not provided enough oxygen to work right and eventually begin to die.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is also known as a “mini stroke.” During TIAs, the blockage in the vessel is only temporary, and symptoms may subside within a few hours. However, a “mini stroke” or TIA indicates a serious underlying issue that may be treated to prevent future risk of a full stroke. If a person arrives at the emergency room within three hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, treatment with a thrombolytic medication can occur that may reduce long-term effects of the stroke and brain injury may be lessened.
Hemorrhagic Strokes
These types of strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain bursts and floods the surrounding brain tissue with blood.This can happen during trauma or as a result of an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a malformation of the blood vessel, which is prone to bursting.
Many people with aneurysm have symptoms prior to the vessel bursting. Some aneurysms can be repaired with surgery prior to bursting. Once a blood vessel bursts in the brain, there are rarely any medications that can be used, and brain surgery may be required to stop further damage.
Statistics:
- Every 40 seconds someone in the U.S. has a stroke – over 900,000 people per year.
- 15% die shortly after stroke.
- 10% recover almost completely.
- 25% recover with mild impairment.
- 40% have moderate to severe impairment requiring special care.
- 10% require a long-term care facility.
Stroke Risk Factors:
- Family history
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Overweight
- Tobacco use
- Race/ethnicity
- Previous stroke or TIA
- Sickle cell disease
- Age (over age 65 males are at higher risk than females)
Stroke Brain Injury Rehab - First Steps
Following the stroke, a person is usually hospitalized to stabilize them medically. At some point during their hospital stay, patients will begin what's called 'acute rehab' or early phase rehabilitation that starts while the patient is overseen around the clock.
- Medical stabilization comes first.
- Depending on medical status, rehabilitative therapy could possibly begin within 24 hours.
- Early rehabilitation has been shown to enhance recovery and minimize functional disability.
- Length of acute rehabilitation depends on severity of stroke, motivation, skill of the treatment professionals, support network, timing and more.
Stroke Brain Injury Post-Acute Rehabilitation
When a patient is ready to be discharged from the hospital, they move to a post-acute rehab facility. This can be an inpatient setting or outpatient. For many stroke brain injury patients, their condition prevents them returning home immediately and they will stay at the rehab facility or its residence so they are monitored by professionals and given help with activities of daily living that they can't yet do: bathing, dressing or even going to the bathroom.
The post-acute rehab phase is determined by the severity of the stroke and the brain injury related deficits.
